SpaceX Eats xAI. OpenAI Eats Cash. Apple Reads Faces.
SpaceX and xAI merge ahead of $1.5T IPO. OpenAI raises $100B at $830B valuation. Apple pays $2B for silent speech tech startup Q.AI.
Chinese researchers abandon AI's rigid think-act-observe loops for fluid reasoning that discovers tools mid-thought. DeepAgent hits 89% success where competitors reach 55%, revealing the bottleneck was never intelligence but architectural rigidity.

Chinese researchers from Renmin University and Xiaohongshu released DeepAgent, an AI system that discovers and uses tools dynamically within its reasoning stream. The approach abandons predetermined workflows entirely. Instead of cycling through "think, act, observe" loops like current agents, DeepAgent treats tool discovery as part of thinking itself, achieving 89% success rates on complex tasks where the best competing models hit 55%.
Previous agents followed scripts: plan the task, select tools, execute actions, observe results, repeat. Even OpenAI's latest research agents work with a fixed toolkit of search, code, and browsing. DeepAgent discovers tools as it reasons. Traditional agents are GPS navigation following predetermined routes. DeepAgent navigates like a local who spots shortcuts mid-journey.
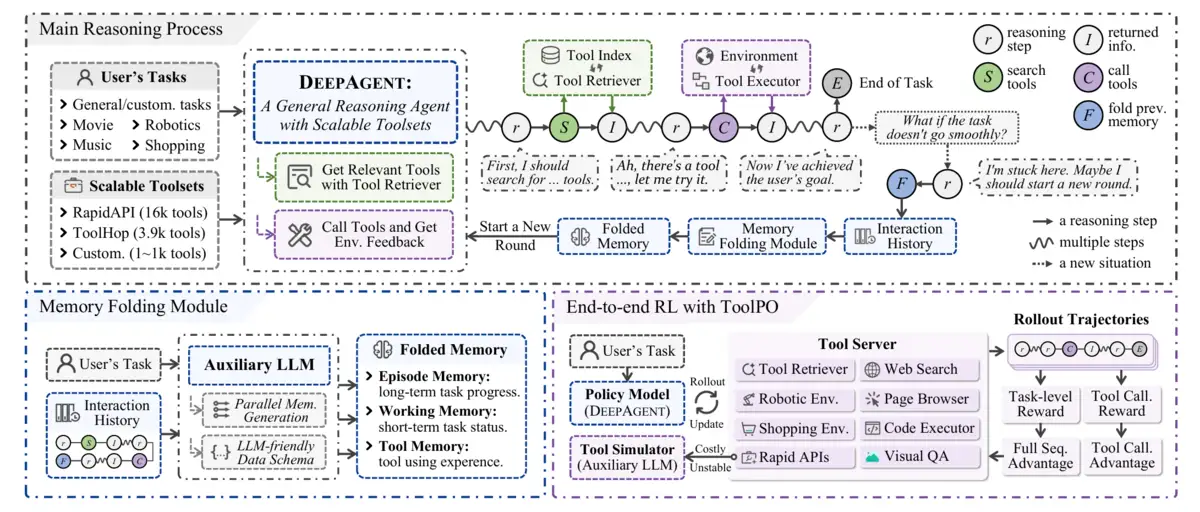
The system can tap 16,000+ real-world APIs without pre-selection. When stuck, it compresses its entire interaction history into structured memory and starts fresh, preventing the death spirals that trap conventional agents in wrong exploration paths.
The Breakdown
• DeepAgent discovers and uses tools dynamically within reasoning, achieving 89% success versus 55% for best competitors
• Memory folding lets agents compress history and pivot when stuck, preventing death spirals in exploration paths
• System taps 16,000+ real APIs without pre-selection while OpenAI limits agents to search, code, and browsing
• Chinese labs now lead autonomous tool use through architectural innovation rather than model size increases
From Beijing's perspective: finally, agent architecture that matches how reasoning models actually think. Western labs built scaffolding around reasoning models, forcing them into rigid cycles. Chinese researchers let reasoning flow naturally.
OpenAI constrains its agents to research tools. Search, browse, code. That's it. DeepAgent pulls from movie databases, music players, robotic environments, shopping APIs, whatever the task demands. The performance gap shows: on Spotify integration tasks, DeepAgent hits 75% success versus 52% for the strongest baseline.
Enterprises get agents that actually work. Previous systems required pre-configuring tool access, defining workflows, managing state transitions. DeepAgent discovers what it needs. A film festival query triggers Vimeo search, identifies cinema professionals, constructs YouTube links, all within one coherent thought stream.
The memory folding mechanism solves a fundamental constraint. Long interactions explode context windows. Agents accumulate interaction history until they can't process new information. Most systems just truncate old data. Information vanishes.
DeepAgent compresses history into three memories: episodic (long-term progress), working (current state), tool (usage patterns). JSON schemas, not prose. Structure preserves precision. When an exploration path fails, the agent folds its memory and pivots. It's controlled forgetting that enables progress.
The training innovation matters. Real APIs break, rate-limit, cost money. DeepAgent simulates them with auxiliary LLMs during training. This trades perfect fidelity for stable, fast, cheap iteration. ToolPO, their reinforcement learning method, assigns credit to specific tool-call tokens rather than whole sequences. Precise feedback accelerates learning.
Three signals determine whether this architecture wins. First, whether memory folding scales beyond 50-action sequences to hundred-step workflows. Current tests stop at 50. Real enterprise processes run longer.
Second, API simulation fidelity. Training on LLM-simulated APIs works until it doesn't. Edge cases, authentication flows, complex state dependencies, these emerge in production. The 89% success rate assumes well-behaved APIs.
Third, tool discovery latency. Searching 16,000 tools mid-thought adds overhead. The paper doesn't report timing. Fast enough for research, but production systems measure milliseconds.
DeepAgent reveals the real bottleneck wasn't reasoning capability but architectural rigidity. Reasoning models can handle complex tool orchestration when freed from predetermined workflows. The constraint was the scaffold, not the model.
Q: How does memory folding actually work when DeepAgent gets stuck?
A: DeepAgent compresses its entire interaction history into three JSON-structured memories: episodic (overall progress), working (current state), and tool (usage patterns). This compression happens after 50 actions or when exploration fails. The agent then restarts with this condensed memory, avoiding previous dead ends while preserving critical information.
Q: What's ToolPO and why does training with fake APIs work?
A: ToolPO (Tool Policy Optimization) uses LLMs to simulate real APIs during training instead of calling actual services. This cuts training costs by 90%+ and prevents rate-limiting issues. The method assigns rewards to specific tool-call tokens rather than entire sequences, making learning 3-5x faster than standard reinforcement learning approaches.
Q: Which specific models did DeepAgent beat and by how much?
A: On ToolBench tasks, DeepAgent (69% success) beat GPT-4o with ReAct (52%), QwQ-32B with CodeAct (54%), and DeepSeek-R1 (57%). On complex GAIA benchmarks, DeepAgent scored 53.3% versus WebThinker's 37% and HiRA's 42.5%. The gaps widen further on music/movie database tasks.
Q: When can developers actually use DeepAgent?
A: The code and demo are available now at github.com/RUC-NLPIR/DeepAgent. It runs on QwQ-32B as the base model with Qwen2.5-32B handling auxiliary tasks. You'll need 64 NVIDIA H20-141GB GPUs for full training, but inference works on smaller setups. The paper was released October 24, 2024.
Q: What real-world tasks does DeepAgent handle better than alternatives?
A: DeepAgent excels at multi-tool coordination: film festival planning (searching Vimeo, finding speakers, linking YouTube), e-commerce workflows (91.8% success on WebShop vs 65.7% for competitors), and embodied AI tasks. It's strongest when tasks need 3-7 sequential API calls across different services, where rigid agents typically fail after 2-3 steps.
Get the 5-minute Silicon Valley AI briefing, every weekday morning — free.