💡 TL;DR - The 30 Seconds Version
👉 Trump imposed a $100,000 fee on new H-1B visa applications Friday, triggering weekend panic as foreign workers abandoned vacations to rush back to the US before Sunday's deadline.
📊 Indian nationals hold 71% of H-1B visas while current fees total just $5,000—making the new charge a 2,000% increase that prices out most smaller companies.
🏭 The fee takes effect Sunday but applies only to new petitions, not renewals or current holders, according to Saturday clarifications from the White House.
🌍 Tech giants like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft sent urgent memos to employees while immigration lawyers warn the policy could relocate innovation to Canada and UK.
⚖️ Legal experts question Trump's authority to impose the fee, calling it "excessive" under federal law that limits agencies to reasonable cost-recovery charges.
🚀 The policy signals a shift toward wealth-based immigration alongside Trump's new "Gold Card" program requiring $1-5 million investments for residency.
Visa fee sparks weekend scramble as workers abandon travel plans. White House clarifications reveal deeper strategic tensions
Trump's Friday afternoon executive order imposing a $100,000 fee on H-1B visa applications triggered an immediate weekend exodus from international airports. Workers on Emirates flights demanded to deplane mid-taxi. Chinese social media filled with "Fast & Furious" references as visa holders abandoned vacations to race back before Sunday's deadline. By Saturday afternoon, the White House was issuing clarifications that suggested either poor coordination or intentional ambiguity.
The immediate trigger was specific: a proclamation requiring new H-1B petitions to include the unprecedented fee, effective Sunday at 12:01 AM Eastern. Current visa holders abroad feared they'd face the charge upon reentry. Tech companies including Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and Goldman Sachs sent urgent memos advising international travel restrictions. The panic was real—and largely unnecessary, as Saturday's clarifications revealed.
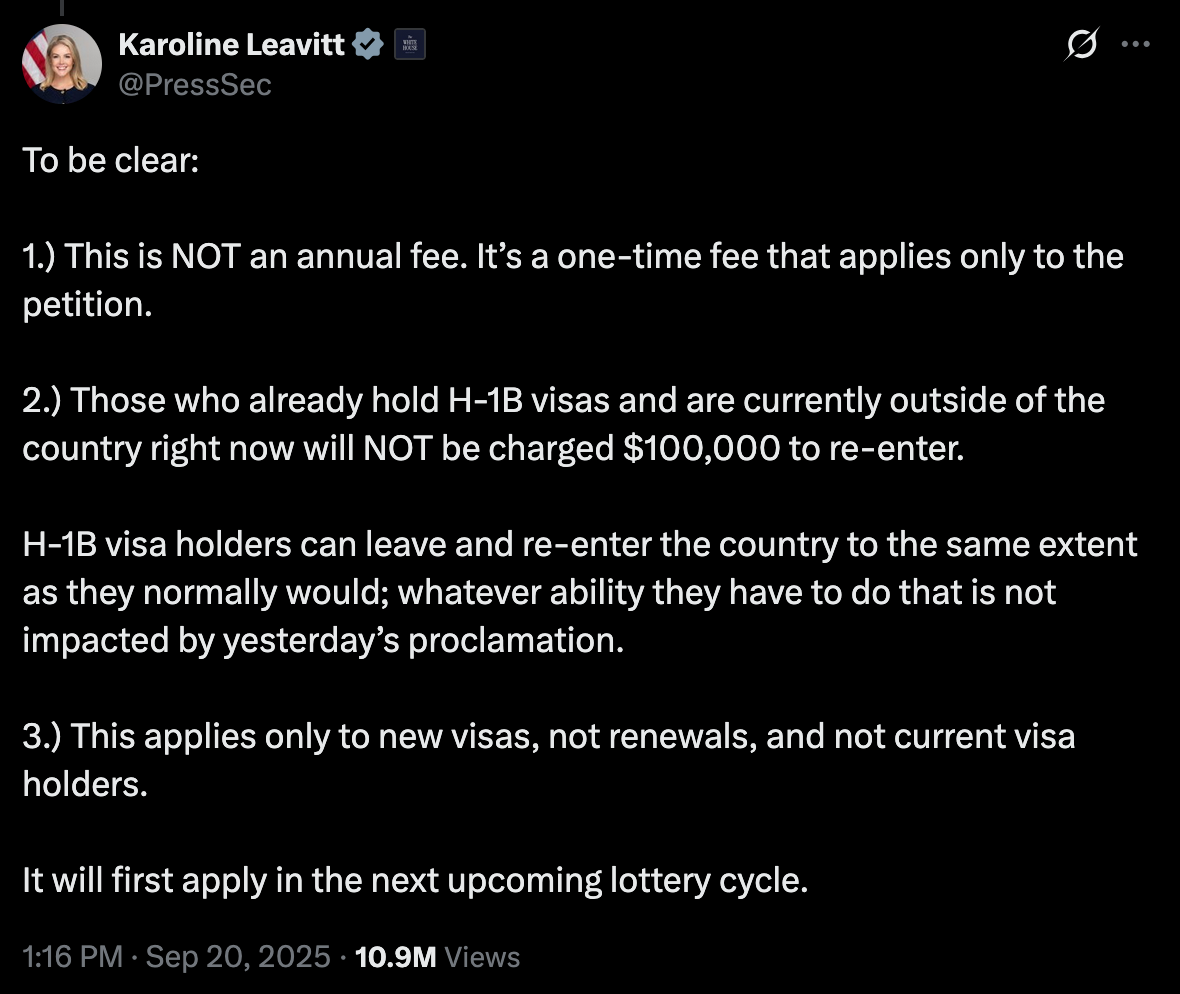
White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt's Saturday afternoon post attempted damage control, specifying the fee applies only to new petitions, not renewals or current holders. But the confusion wasn't entirely accidental. The sequence revealed the administration's broader immigration philosophy: a deliberate shift toward class-based access that favors wealth over skill alone.
The architecture of selective access
The H-1B chaos obscured Trump's simultaneous announcement of "Gold Card" visas—$1 million for individual residency, $2 million for corporate sponsorship, and a forthcoming "Platinum" option at $5 million for 270-day annual access without US tax obligations. The timing wasn't subtle: restrictions on traditional skilled immigration paired with express lanes for the wealthy.
From the administration's perspective, this represents long-overdue market correction. Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick framed the choice starkly: "Is the person valuable enough to have a $100,000-a-year payment to the government, or they should head home and go hire an American?" The White House fact sheet claimed American workers face replacement by "lower-paid foreign labor," calling it a national security threat.
From Silicon Valley's view, the policy creates artificial scarcity that damages US competitiveness. Y Combinator's Garry Tan noted early-stage teams "can't swallow that tax." Immigration attorney Sophie Alcorn described companies splitting into those who "can afford to basically pay to play" and smaller firms unable to compete. The talent doesn't disappear—it relocates to Toronto, Vancouver, London.
Both readings have merit. The H-1B program has enabled wage suppression in some sectors while filling genuine skill gaps in others. The $100,000 fee addresses the former by pricing out routine applications, but potentially worsens the latter by reducing overall talent inflow.
Legal authority questions and implementation chaos
The weekend's confusion exposed fundamental questions about what the administration can actually do. Most H-1B applications currently cost around $5,000 total—fees designed to cover government processing costs. Federal statutes generally restrict agencies to charging what's needed for reasonable cost recovery.
Vermont immigration attorney Becky Fu von Trapp called the $100,000 charge potentially "excessive" under existing law. Immigration lawyer David Leopold warned this approach could "effectively kill the program" while facing inevitable court challenges. The American Immigration Council's Aaron Reichlin-Melnick was blunt: "The president has literally zero legal authority to impose a $100,000 fee on visas."
The administration appears to be betting on presidential proclamation powers rather than formal rulemaking. That's a risky legal strategy, though recent Supreme Court decisions have made nationwide injunctions harder to obtain. The policy could operate for months during litigation. There's also a "national interest" exemption allowing case-by-case fee waivers—another potential legal defense.
Still, charging twenty times the normal fee to recover processing costs seems like a stretch. Immigration attorneys expect quick court challenges.
The talent redistribution reality
The structural impact extends well beyond individual cases. Indian nationals represent 71% of H-1B approvals, with China at 11.7%. The fee immediately disrupts Indian IT services companies that deploy thousands of professionals annually. But it also accelerates talent migration to countries actively courting skilled workers.
Outreach co-founder Manny Medina, recently relocated to London, posted directly to "founder friends stuck in visa limbo: London's doors are open." Canada's startup visa program and the UK's Global Talent route offer alternative pathways without prohibitive fees. The US risks recreating what economist Neil Bradley called the pandemic-era dynamic: "Businesses having to turn down work because they simply can't find the workers to do it."
The policy also reshapes internal US talent distribution. Large technology companies can absorb the costs for critical hires, potentially concentrating skilled immigration among tech giants while smaller companies lose access entirely. Amazon sponsored over 9,000 H-1B visas in fiscal 2024, Google 5,364, Meta 4,844—numbers that reflect substantial but manageable financial exposure at the new fee levels.
Early-stage companies face different math entirely. A startup burning $50,000 monthly can't easily justify $100,000 for a single hire, regardless of their qualifications.
Political dynamics and coalition tensions
The H-1B changes reflect ongoing tensions within Trump's coalition. Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy have defended H-1B programs as essential for innovation, while Steve Bannon characterizes them as "scams" by Silicon Valley titans creating "indentured servants at lower wages." The $100,000 fee attempts to split this difference—maintaining the program while making it prohibitively expensive for routine use.
Congressional intervention seems unlikely despite some pressure. Immigration legislation remains challenging even with narrow Republican majorities. The party's business wing wants more high-skilled immigration while its populist wing seeks restrictions across the board. Democrats have little incentive to help given ongoing ICE enforcement escalations in major cities.
That leaves the administration operating through executive orders and proclamations—faster but legally riskier than legislation. The weekend's implementation chaos suggests they're testing how much disruption they can create before clarification.
The emerging equilibrium
The weekend's panic revealed the administration's immigration vision: deliberate scarcity enforced through pricing rather than caps. This approach maintains legal immigration pathways while ensuring only the highest-value applications proceed. Whether that calculus serves broader economic interests depends on whether reduced immigration volume improves wages for American workers or simply relocates innovation elsewhere.
The implementation confusion could reflect administrative incompetence or strategic ambiguity designed to maximize disruption before clarification. The latter interpretation fits the broader pattern of using uncertainty as policy enforcement.
What's clear is the structural shift underway. US immigration policy increasingly resembles investor visa programs, prioritizing wealth over skills alone. The Gold Card program requires no skill demonstration beyond financial capacity, while skilled workers face growing barriers regardless of qualifications.
For companies and workers caught in the transition, the message seems deliberate: adapt to the new pricing structure or find alternatives elsewhere. The global talent market will adjust accordingly.
Why this matters:
• Immigration as class filter: The US is deliberately creating a two-tier system where wealth matters more than skills, potentially undermining long-term competitiveness in knowledge industries where talent concentration drives innovation
• Permanent talent migration: Other countries offering clearer, cheaper pathways may capture skilled workers displaced by US restrictions, creating lasting advantages for competitor nations that could take decades to reverse
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does the $100,000 fee compare to what companies pay now?
A: Current H-1B applications cost around $5,000 total in government fees and legal costs. The new fee represents a 2,000% increase, making it one of the highest visa fees globally. Even complex investment visas typically cost under $10,000.
Q: Which companies will be hit hardest by this change?
A: Startups and smaller companies face the biggest impact since they can't absorb $100,000 per hire. Large tech companies like Amazon (9,000+ H-1B visas in 2024) and Google (5,364 visas) can likely manage the costs for critical roles.
Q: When exactly does this policy start and how long does it last?
A: The fee takes effect Sunday, September 21, 2025 at 12:01 AM Eastern. It applies only to new H-1B petitions filed after that time. The policy automatically expires on September 21, 2026 unless extended.
Q: Can companies avoid paying the $100,000 fee?
A: Yes, through a "national interest" exemption that allows case-by-case fee waivers at the Secretary of Homeland Security's discretion. However, the criteria for exemptions haven't been defined, making this option unpredictable for employers.
Q: What happens to people who already have H-1B visas?
A: Current H-1B holders are unaffected. They can travel and re-enter the US normally, and renewals don't require the $100,000 fee. The charge applies only to completely new applications for workers who don't currently have H-1B status.










