Good Morning from San Francisco,
OpenAI, Meta, and Google launched a coordinated assault on state AI regulations. They secured federal language threatening funding cuts to "unduly restrictive" states. The charm offensive worked.
Colorado's algorithmic discrimination law crumbled under pressure. Even Governor Polis wants changes. Meanwhile, states introduced over 1,000 AI bills because Congress won't act. Most bills are theater. Some have teeth.
Nick Clegg's Meta exit speaks volumes. He watched the industry transform from politically wary to politically captured. The former UK Deputy PM called out Silicon Valley's victim complex. Meta spends $70 billion annually on AI—more than most countries' budgets. Yet executives whine about oversight.
Stay curious,
Marcus Schuler
Colorado's pioneering law faces major revisions

Tech companies including OpenAI, Meta, and Google have launched a coordinated campaign to block state AI regulations, successfully securing language in Trump's July AI plan that restricts federal funding to states with "unduly restrictive" AI rules.
The strategy represents calculated adaptation rather than blanket opposition.
Over 1,000 state AI bills were introduced in 2025, though only several dozen impose substantive regulatory requirements. The volume suggests legislative urgency while most remain procedural gestures. States are moving because Congress won't.
Two distinct regulatory models have emerged. Nevada and Illinois ban AI from providing professional mental health services, creating enforcement challenges for general-purpose systems. California's SB 53 and New York's RAISE Act require transparency from the largest AI developers without dictating technical approaches.
Colorado's algorithmic discrimination law exemplifies the pressure dynamics. Initially scheduled for February 2026 implementation, it now faces revision in special session after industry warnings of "severe economic costs." Even Democratic Governor Polis called for changes.
The coordination reflects strategic geography. Companies can absorb multi-state compliance costs and credibly threaten relocation, while startups cannot.
Why this matters:
• Regulatory geography now drives business strategy: Companies can absorb multi-state compliance costs and credibly threaten relocation, creating structural advantages over startups that cannot
• Federal funding becomes policy leverage: White House restrictions on "unduly restrictive" states provide soft power to reshape regulations without congressional action

AI Image of the Day

Prompt:
A photograph of an elderly man with a kind face and
weathered hands gently embracing a baby orangutan. The man is wearing a worn, brown tweed hat that sits playfully atop the orangutan's head. They are positioned in a sun-drenched, lush rainforest clearing, with vibrant green foliage creating a soft backdrop. Warm, golden sunlight filters through the canopy, illuminating the tender moment and highlighting the textures of the man's skin and the orangutan's soft fur, conveying a sense of deep affection and mutual comfort.
Former policy chief warns AI power outpaces democracy

Nick Clegg announced his Meta departure in January 2025. Weeks later, Silicon Valley's biggest names appeared at Trump's inauguration like schoolchildren awaiting photos.
The timing wasn't coincidental—Clegg had watched the industry transform from politically wary to politically captured.
From the Valley's perspective, Trump alignment offers regulatory relief and China partnership opportunities. From Washington's view, controlling AI infrastructure requires tech sector loyalty. From Clegg's European background, this represents democratic capture by private interests. All three readings work simultaneously.
Clegg's sharpest critique targets Silicon Valley's victim complex. Despite immense wealth, tech leaders increasingly see oversight as persecution. Meta alone spends $70 billion annually on AI infrastructure—more than most countries' entire budgets.
The sequence reveals structural transformation. When platforms become partisan actors while claiming neutrality, they undermine their social license to operate as democratic infrastructure.
Why this matters:
• Tech's political alignment demonstrates how AI infrastructure power converts directly into political leverage, challenging platform neutrality claims
• Democratic governance requires institutional frameworks matching AI-era scale, not just corporate self-regulation initiatives

🧰 AI Toolbox
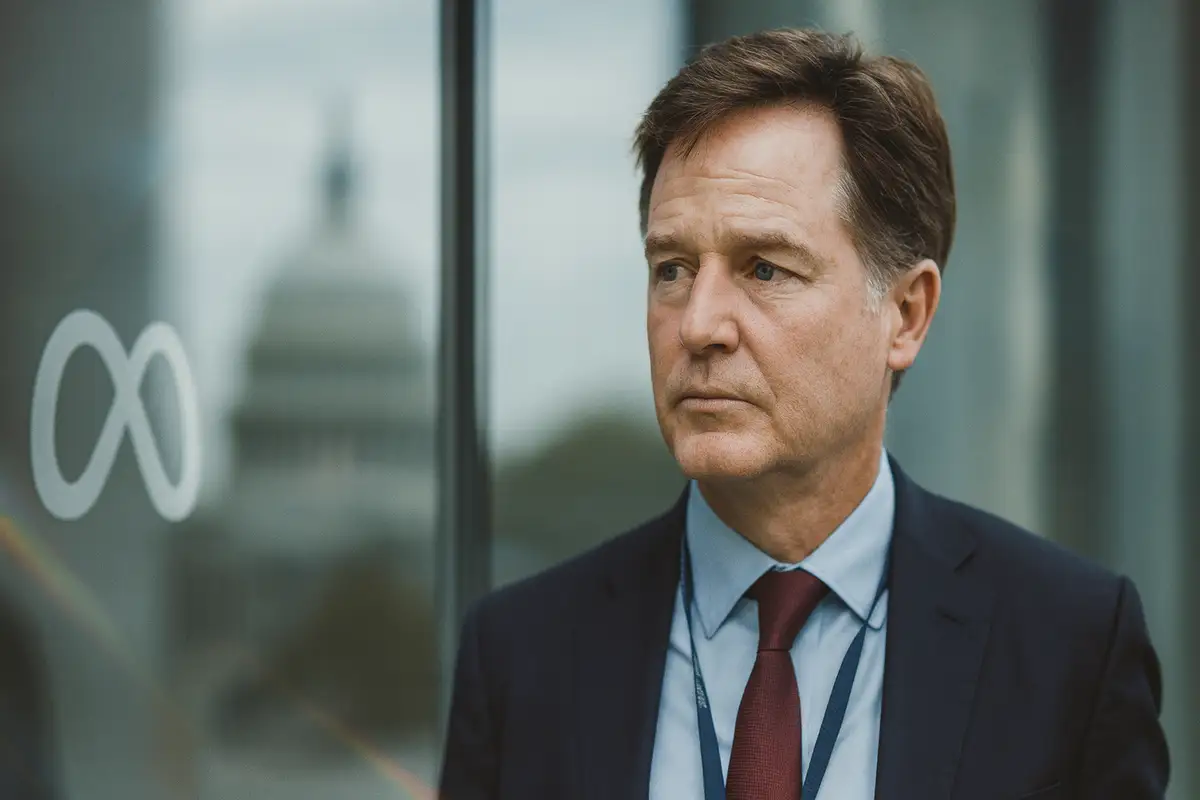
How to Create Technical Diagrams and Documentation with AI
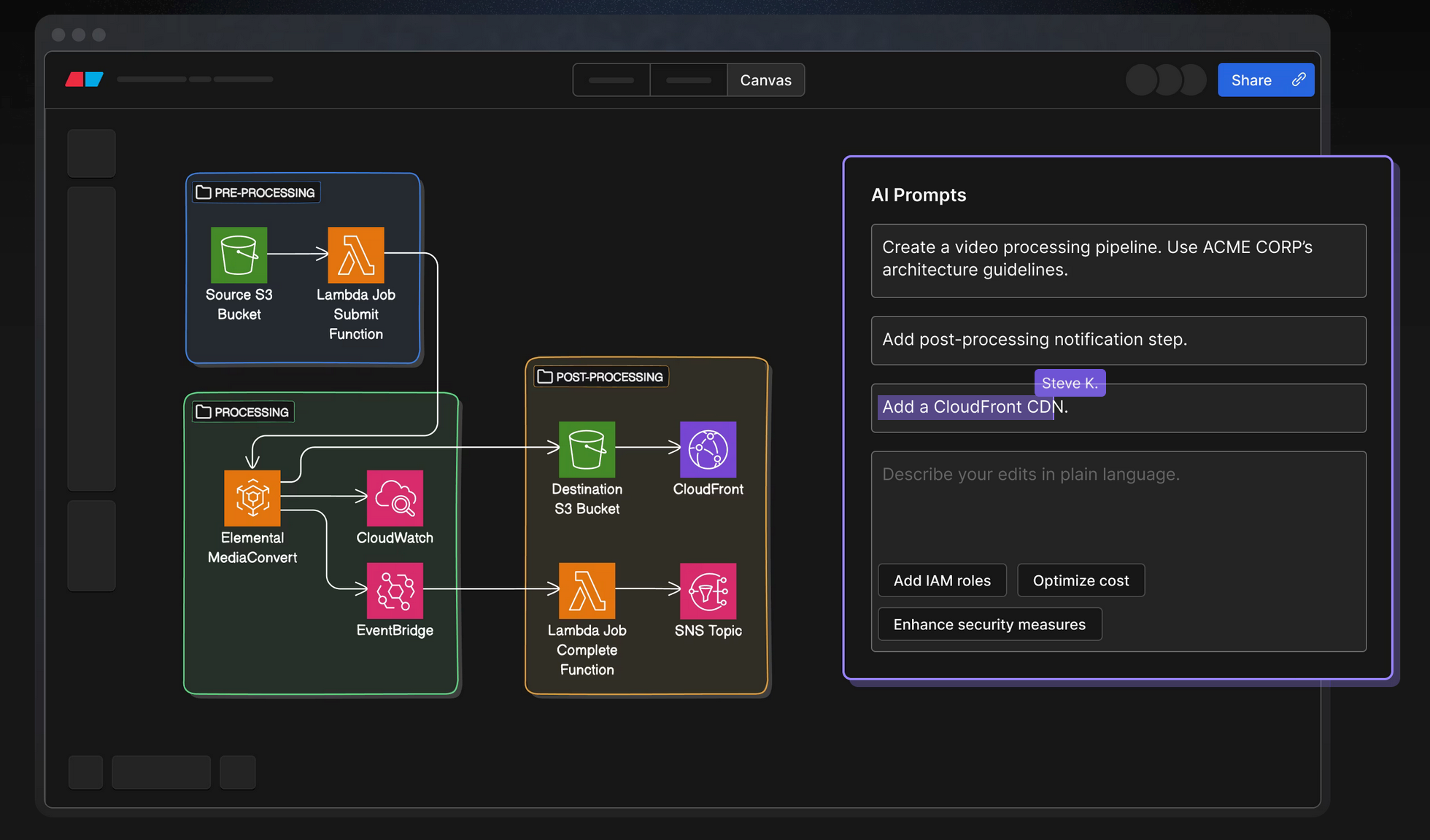
Eraser creates technical diagrams and documentation for engineering teams using AI-powered tools. Generate flow charts, sequence diagrams, cloud architecture diagrams, and more from simple text prompts, then collaborate in real-time with your team.
Tutorial:
- Go to the Eraser website
- Create a free account and start a new file
- Use DiagramGPT to generate diagrams from text prompts or code snippets
- Edit and customize your AI-generated diagrams with the visual editor
- Add technical documentation using the markdown-compatible note editor
- Collaborate with teammates in real-time and sync to GitHub repositories
- Export your work or integrate with tools like Confluence and Notion
AI & Tech News
Perplexity Comet vulnerability breaks traditional security barriers
Brave researchers discovered attackers can embed malicious prompts in web content—like Reddit comments—that trick Perplexity's Comet AI browser into stealing login credentials and accessing private accounts when users simply ask it to summarize a page. The attack renders standard web security protections like same-origin policy useless because the AI operates with full user privileges across all authenticated sessions.
Tech giants mobilize for midterm elections defense campaign
Silicon Valley is putting over $100 million into a network of political action committees called Leading the Future, with Andreessen Horowitz and OpenAI President Greg Brockman among the backers launching the effort to oppose strict AI regulations ahead of next year's midterm elections. The move creates the first major organized political counterforce to AI safety advocates, potentially reshaping how Congress approaches artificial intelligence policy as the technology race with China intensifies.
TSMC strips Chinese equipment from most advanced chip lines
TSMC is removing all Chinese chipmaking equipment from its most advanced 2-nanometer production lines that begin mass production this year, driven by potential US regulations like the proposed Chip EQUIP Act that would bar recipients of federal funding from using Chinese manufacturing tools. The move signals how geopolitical tensions are forcing chipmakers to restructure not just where they make chips, but which suppliers they trust with their most critical production processes.
xAI open sources Grok 2.5 model weights on Hugging Face
Elon Musk's xAI released the model weights for Grok 2.5 on Hugging Face, with Musk saying Grok 3 will follow in about six months despite the current license containing "anti-competitive terms." The move pressures other AI companies to match xAI's open source timeline or risk appearing secretive as the industry debates whether releasing powerful models helps or harms competitive positioning.
DHL's AI voicebot couldn't recognize German word for "yes"
DHL discovered its upgraded AI voicebot failed to recognize "Ja"—German for "yes"—during transcript reviews, exposing how basic language gaps persist even in million-call-per-month systems. The glitch highlights the complexity of AI deployment as companies race to automate processes before one-third of their workforce retires within five years, forcing retraining over replacement to address labor shortages.
Spotify signals more price hikes as streaming wars shift to profit
Spotify will continue raising subscription prices as "part of our toolbox now" while adding new features and targeting 1 billion users, co-president Alex Norström told the Financial Times, marking a shift from the company's years of flat pricing that helped deliver its first annual profit in 2024. The move signals streaming platforms are abandoning growth-at-all-costs strategies for pricing power, potentially reshaping how the industry balances subscriber acquisition with profitability as competition intensifies.
Netflix opens physical entertainment venues this November
Netflix will open its first permanent entertainment venues November 12 in Philadelphia and December 11 in Dallas, featuring 100,000-square-foot spaces with paid experiences based on hits like Squid Game and Stranger Things. The move shows how streaming companies are building physical spaces to monetize their content beyond screens, turning popular shows into immersive experiences that could reshape entertainment retail.
Mobile-first streaming overtakes traditional platforms with algorithm-driven content
DramaBox, a vertical streaming app featuring 60-second soap opera episodes with titles like "Dominated by My Dad's Boss," now has 44 million monthly users—more than Hulu or Paramount+. The shift signals traditional streaming platforms are losing ground to mobile-first entertainment that uses TikTok-style algorithms and charges users up to $200 monthly for bite-sized melodrama optimized for short attention spans.
KnowledgeLake raises $65M for AI document automation
KnowledgeLake raised $65 million led by Edison Partners to expand its AI-powered document processing platform that serves 220+ mid-sized businesses and government agencies, including the states of Tennessee and Kentucky. The funding signals venture capital is backing "synthetic labor" companies that automate white-collar work beyond large enterprises, potentially reshaping how smaller organizations compete with automation traditionally reserved for Fortune 500 companies.
🚀 AI Profiles: The Companies Defining Tomorrow
KnowledgeLake
KnowledgeLake turns documents into action without humans. The St. Louis company just raised $65 million to prove "Synthetic Labor" beats manual data entry.
The founders
• Founded: 1999 by Ron Cameron and Bob Bueltmann in St. Louis, Missouri
• Current status: Kevin Herr became CEO in August 2025; Cameron moved to advisor role
• Why: Help businesses work better through technology (started as Microsoft SharePoint specialists)
The product
• Core offer: AI-powered document automation platform that captures, classifies, extracts, and completes tasks
• Strengths: One platform handles IDP + workflow + RPA instead of stitching three tools together
• What it does: Bots read invoices, fill forms, route approvals, and click through legacy systems without APIs
• Sweet spot: Microsoft-native deployments in government and mid-market
The competition
• IDP players: ABBYY, Hyperscience, Rossum, Tungsten Automation
• RPA giants: UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism (all adding document smarts)
• Suite threats: Microsoft SharePoint Premium, Hyland OnBase, OpenText
• Differentiation: Unified platform, Microsoft integration, public-sector focus via Carahsoft channel
Financing
• Latest round: $65M majority growth investment from Edison Partners (August 2025)
• Previous: Self-funded through sales, 2018 buyback with Plymouth Growth Partners
• Valuation: Undisclosed
• Traction: 220+ customers, 50%+ SaaS growth, 95% retention
The future ⭐⭐⭐⭐
KnowledgeLake bets Microsoft shops want fewer vendors, not more features. The CEO switch from founder to operator should sharpen execution. If the team proves "synthetic laborers" work reliably, city halls will keep buying. If not, the suites absorb the functionality and KnowledgeLake becomes a feature comparison footnote. 📋










